Simkovic I, Hricovini M, Soltes L, Mendichi R, Cosentino C. Preparation of water soluble/insoluble derivatives of Hyaluronic acid by cross linking with epichlorohydrin in aqueous NaOH/NH4OH solution. Peer D, Margalit R. Physicochemical analysis of a stability-driven approach to drug entrapment in regular and in surface-modified liposomes. Morimoto K, Yamaguchi H, Iwakura Y. Effects of viscous hyaluronate-sodium options on the nasal absorption of vasopressin and an analog. Morimoto K, Metsugi K, Katsumata H. Effects of lowviscosity sodium hyaluronate preparation on the pulmonary absorption of rh-insulin in rats.
Consistently lowered nerve supply is seen in synovial tissue from RA sufferers, particularly in the more superficial intimal regions. Guidolin DD, Ronchetti IP, Lini E. Morphological evaluation of articular cartilage biopsies from a randomized. Clinical research evaluating the consequences of 500–730 kDa sodium hyaluronate Hyalgan and methylprednisolone acetate on main osteoarthritis of the knee. Fraser JRE, Kimpton WG, Pierscionek BK, Cahill RNP. The kinetics of hyaluronan in regular and acutely inflamed synovial joints – observations with experimental arthritis in sheep. Dahl LB, Dahl IM, Engstrom-Laurent A, Granath K. Concentration and molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Low-molecular weight HA was found to exert different biological actions compared to the native high-molecular-weight biopolymer.
Synovial Membrane, Synoviocyte, Hyaluronic Acid, Lubricin
Moreira CA, Moreira AT, Armstrong DK.In vitro and in vivo studies with sodium hyaluronate as a provider for intraocular gentamicin. Moreira CA, Armstrong DK, Jelliffe RW. Sodium hyaluronate as a service for intravitreal gentamicin – an experimental examine. Miyazaki M, Sato S, Yamaguchi T. Analgesic and antiinflammatory action of hyaluronic sodium; Japan Pharmacological Conference; April four, 1983; Tokyo. Lim ST, Forbes B, Berry DJ, Martin GP, Brown MB. In vivo evaluation of novel hyaluronan/chitosan microparticulate supply techniques for the nasal delivery of gentamicin in rabbits. Langer K, Mutschler E, Lambrecht G. Methylmethacrylate sulfopropylmethacrylate copolymer nanoparticles for drug delivery – Part III. Evaluation as drug delivery system for ophthalmic functions. Kemmann E. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and assisted reproductive expertise – quantification of risks as part of informed consent.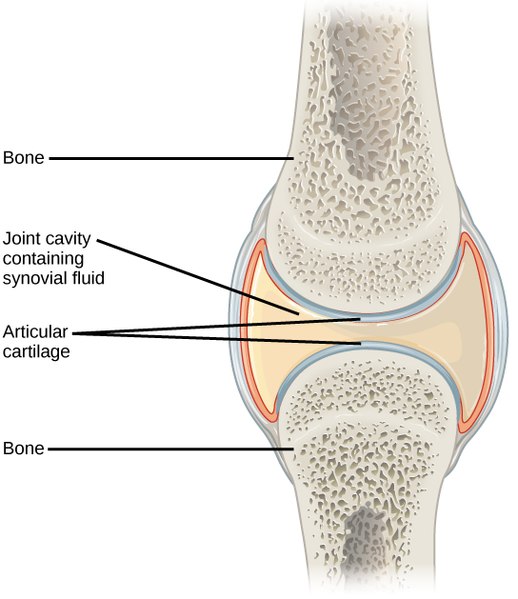
Tendons are powerful bands of fibrous connective tissue that connect muscles to bones. The bones of a synovial joint are surrounded by a synovial capsule, which secretes synovial fluid to lubricate and nourish the joint whereas appearing as a shock absorber. This fluid is generated from an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma which is regulated by synovium.
Synovial Membrane, Synovial Fluid, And Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells
This mechanism to form a protecting layer is much less effective in arthritis when the synovial hyaluronan has each a decrease focus and a decrease molecular weight than regular. Another change within the arthritic joint is the protein composition of the synovial fluid. Fraser et al. confirmed more than 40 years ago that addition of varied serum proteins to hyaluronan substantially increased the viscosity and this has obtained a renewed curiosity in view of recently discovered hyaladherins . TSG-6 and inter-α-trypsin inhibitor and other acute section reactants such as haptoglobin are concentrated to arthritic synovial fluid (Hutadilok et al.,1988).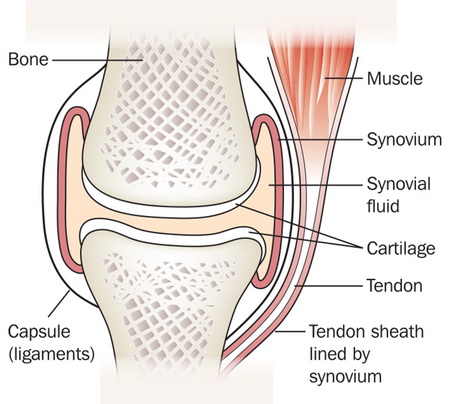
The synovial fibroblasts may make smaller hyaluronan so it’s a less effective lubricant of the cartilage surfaces. Under stimulation from invading inflammatory cells, the synovial cells may also produce enzymes that may digest the cartilage extracellular matrix. Fragments of extracellular matrix can then additional irritate the synovium.
What Is A Synovial Joint?
The arachnoid is hooked up to the dura mater, whereas the pia mater is hooked up to the central nervous system tissue. The intimal cells are termed synoviocytes and are of two varieties, fibroblastic and macrophagic . Most mucous membranes contain stratified squamous or easy columnar epithelial tissue.